The Importance of Early Detection: How to Identify Gum Disease Symptoms
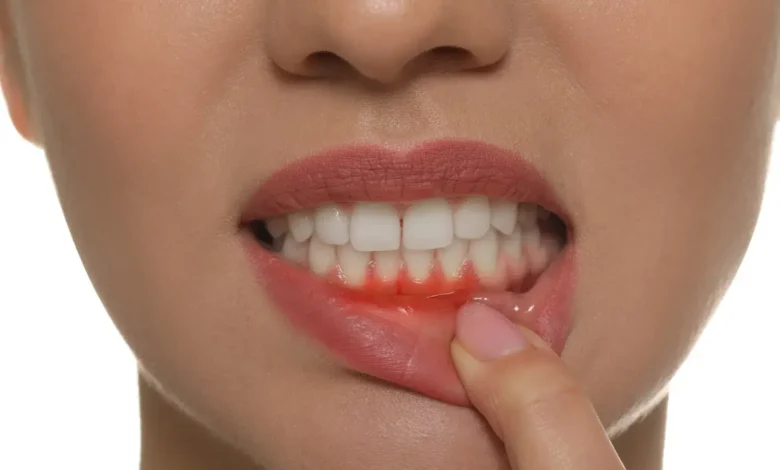
Periodontal or gum disease is among the most common dental disorders. Unfortunately, it is hard to detect in the early stages. However, without gum treatment, one can face serious consequences, such as loss of teeth, deterioration of the jaw, and other complications.
If noticed by the dentist in time and with the right diagnosis and treatment, the disease can be controlled, and a patient can avoid further complications. Thus, early detection is very important to keep oral health.
Understanding Gum Disease
Periodontitis is an infectious disease caused by the destructive bacteria that affect gums and the supporting structure of the teeth. It is usually initiated as gingivitis, which is the mildest form of periodontal disease, involving inflammation and irritation of the gums. In case of no treatment or advanced stage, gingivitis may progress into periodontitis, which is a more serious and destructive form of the disease when bones and tissues that surround and support teeth are infected.
Why Is Early Detection Crucial?
Since gum disease has serious long-term effects on one’s general health, early diagnosis is paramount. The first symptoms are usually painless and easily ignored; thus, most people only seek medical help when symptoms worsen and discomfort sets in. Early detection of gum disease allows for early intervention that can prevent permanent damage.
The majority of gum disease cases are treatable using quite simple, non-invasive approaches, which include professional cleaning, scaling, and root planing. These methods help remove plaque and hardened tartar deposits, reducing inflammation. However, if the disease has advanced, only surgery or bone grafting can repair the diseased tissue.
Recognizing Common Symptoms of Gum Disease
Awareness of the symptoms is the first step to early detection. Here are a few signs indicating that you are at high risk for developing gum disease:
- Bleeding gums. Bleeding, especially while brushing or flossing, is a clear symptom of gum disease. People often do not regard it as serious and can overlook this sign; however, frequent and persistent bleeding is a critical indicator of inflammation or infection in the gums.
- Bad breath. Many factors can cause bad breath. If bad breath persists despite good oral hygiene habits such as brushing and flossing, it may be a sign of periodontal disease. Infected gum tissue is an environment for bacterial impact on foods, which results in the production of odorous compounds. So, this infection may lead to chronic bad breath.
- Receding gums. Advanced gum disease may cause gums to recede or pull away from teeth, exposing more of the teeth root. This can make the teeth appear “longer” and cause sensitivity. It is a serious symptom of periodontitis that requires immediate attention.
- Loose teeth. The advancing disease may spread into the bones and ligaments that support teeth, and they can start loosening or displacing from their socket. Affected teeth may fall out with time if proper care is not taken.
Preventing Gum Disease
Gum disease can be prevented by regular, proper oral hygiene. To remove plaque buildup, you need to brush teeth at least twice a day and floss once a day. Regular dental visits, preferably every six months, can help spot gum disease early and clean areas that may be difficult to reach. In addition, stopping smoking can significantly decrease the risk of periodontal disease. A healthy diet with necessary vitamins and minerals also contributes to the normal condition of gums as well as the general strengthening of the immune system.
Preventive measures, coupled with the detection of early warning signs of gum disease, may help avoid serious oral health issues. Don’t miss the onset of the disease, and be informed about its early signs and symptoms to keep your teeth healthy.
